-

GZY-D840
4Ports UHF RFID Reader4-Port RFID Split-Type Reader for Industrial-Grade Reliability, Lightning-Fast Identification, and Dual-Protocol CompatibilityView Details -

GZY-E609
High-Performance RFID Integrated ReaderUltra-high frequency integrated reader series, high-performance RFID integrated reader, all-weather operation, stable long-distance reading, applicable to access control, logistics and other applications.View Details -

GZY-33
USB Tablet Desktop RFID ReaderSpecialized RFID reading and writing station for physical evidence, with a 400mm large surface and adjustable power of 33dBm.View Details -

GZY-T509
9dbi RFID Circularly Polarized AntennaRFID ultra-high frequency 9dBi antenna, with strong anti-aging and weather resistance, capable of stable operation in harsh environments.View Details -

GZY-202
UHF RFID Handheld RederRFID handheld terminal reader, with high processing performance, long tag reading distance and high group reading rate, is widely used in logistics, asset management and other scenarios.View Details -
GZY-122
1-2M Android RFID Handheld RederRFID handheld terminal reader, with high processing performance, Multifunctional RFID warehouse inventory handheld device, integrating RFID and biometric identification,with excellent performance and stability.View Details -
GZY-E98
8Port RFID Reader ModuleView Details -

GZY-R1808
Printable small anti-metal RFID labelRFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse managementView Details -

GZY-R6025
Custom anti-metal RFID labelRFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse managementView Details -

GZY-P8020
7m long distance uhf rfid tag7-meter ultra-long-range PCB anti-metal tags, with industrial-grade protection, an excellent tool for warehouse shelf managementView Details -
GZY-A13042
12m UHF Rugged RFID TagsView Details -
GZY-A20043
35m Long Distance RFID Hard Metal TagsView Details -

GZY-X5012
UHF RFID laundry tagView Details -
GZY-Z30
Plastic RFlD Tracking Seals TagRFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse managementView Details -
GZY-Z4028
RFID Anti-Theft Security Seals TagView Details


- Home
-
Power & Grid
-
Infowise RFID
Product Number
GZY-P8020
GZY-P8020
7-meter ultra-long-range PCB anti-metal tags, with industrial-grade protection, an excellent tool for warehouse shelf management
GZY-P2510
GZY-P2510
Ultra-thin anti-metal PCB tags, a powerful tool for managing metal equipment/tool assets
GZY-P0505
GZY-P0505
Micro anti-metal PCB tags, stable reading of items on metal surfaces, industrial-grade IP68 protection
GZY-P305
GZY-P305

GZY-P1207
GZY-P1207
High-performance PCB anti-metal electronic tags, stable reading for metal surface items
GZY-P1309
GZY-P1309
RFID asset management PCB tags, stable reading and writing in extreme environments, suitable for medical devices/asset management
GZY-P1616
GZY-P1616
RFID equipment manages electronic tags, with stable reading and writing performance in extreme environments, suitable for equipment/asset management.
GZY-P1809
GZY-P1809
RFID anti-metal electronic tag, UCODE 8 chip, IP68 protection, extreme temperature tolerance
GZY-P2208
GZY-P2208
Ultra-high frequency anti-metal PCB tag, metal surface 4.5 meters precise recognition, industrial-grade durable design
GZY-P2309
GZY-P2309
Industrial-grade PCB anti-metal tags, remaining functional in harsh environments
GZY-P3005
GZY-P3005
Ultra-thin anti-metal PCB tags, a powerful tool for managing metal equipment/tool assets
GZY-P3612
GZY-P3612
RFID mine personnel positioning tag, industrial-grade metal-resistant, suitable for harsh environments
GZY-P5010
GZY-P5010
PCB anti-metal RFID inspection tag, 5.5-meter mobile recognition, unaffected by oil stains and vibrations
GZY-P7020
GZY-P7020
Ultra-long-range 9-meter PCB anti-metal tag, with industrial-grade protection, suitable for large equipment/warehouse management
GZY-P9525
GZY-P9525
10.5-meter ultra-long-range PCB anti-metal tags, specially designed for industrial-grade heavy equipment management
GZY-P0904
GZY-P0904
PCB fixed asset electronic tags, stable reading of items on metal surfaces, IP68 protection suitable for harsh environments
GZY-P1005
GZY-P1005
Small-sized PCB anti-metal tag, IP68 protection, 50-year data retention
GZY-P1307
GZY-P1307
Tool management RFID anti-metal PCB tags, stable reading and writing in extreme environments, suitable for equipment/asset management
GZY-P1504
GZY-P1504
RFID anti-metal PCB passive electronic tag, stable reading and writing in extreme environments, suitable for equipment/asset management
GZY-P1806
GZY-P1806
PCB anti-metal RFID tags, stable reading and writing in extreme environments, suitable for devices/asset management
GZY-P305
GZY-P305
Locatable RFID anti-metal PCB tags with fast, accurate and stable reading/writing capabilities Product Number
Product NumberGZY-R1808
GZY-R1808
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R6025
GZY-R6025
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R3015
GZY-R3015
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R3012
GZY-R3012
RFID flexible printable electronic tags, optimized for metal surface applications, compatible with non-metal surfaces
GZY-R4025
GZY-R4025
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R5015
GZY-R5015
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R5025
GZY-R5025
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R6505
GZY-R6505
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R6535
GZY-R6535
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R7025
GZY-R7025
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R7030
GZY-R7030
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-R8025
GZY-R8025
UHF flexible anti-metal tag, equipped with Impinj Monza R6/M730 chip, capable of 100,000 write-erase cycles,with 10-year data storage capacity
GZY-R8040
GZY-R8040
High and low temperature resistance flexible label, With a wide temperature range of -40°C to +120°C, IP68 protection against moisture and corrosion, suitable for harsh environments
GZY-R9522
GZY-R9522
Industrial-grade weather-resistant RHID flexible labels, with a reading distance of up to 5 meters on metal surfaces
GZY-R10040
GZY-R10040
Large-sized flexible RFID electronic tags, used in scenarios such as IT assets, automotive parts, and warehouse logistics management
GZY-R8020
GZY-R8020
9.5-meter ultra-long-range PCB anti-metal tags, with industrial-grade protection, an excellent tool for warehouse shelf management
GZY-R8050
GZY-R8050
无GZY-R5515
GZY-R5515
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management Product Number
Product NumberGZY-X5012
GZY-X5012

GZY-X1818
GZY-X1818

GZY-X2020
GZY-X2020

GZY-X2525
GZY-X2525

GZY-X5815
GZY-X5815

GZY-X7015
GZY-X7015

GZY-X7512
GZY-X7512
Ultra high-frequency RFID clothing labels that have withstood 200 industrial washes at 180°C, with anti-theft protection during sewing installation.
GZY-X8616
GZY-X8616
Product NumberGZY-A13042
GZY-A13042
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A20043
GZY-A20043
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A105
GZY-A105
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A6923
GZY-A6923
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A8724
GZY-A8724
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A8520
GZY-A8520
Long-distance RFID anti-metal tag, 12 meters long range IP68 protection, -40°C corrosion-resistant with 100,000 times write erase cycles
GZY-A8724
GZY-A8724
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-A9525
GZY-A9525
RFID ultra-thin anti-metal tag, 12-meter long-range, IP68 protection, -40°C corrosion-resistant, 100,000 times write erase cycles Product NumberProduct Number
Product NumberProduct NumberGZY-Z30
GZY-Z30
RFID flexible anti-metal tags, with back adhesive application design, suitable for scenarios such as asset and warehouse management
GZY-Z4028
GZY-Z4028

GZY-C11045
GZY-C11045
GZY-C8554
GZY-C8554
GZY-M6617
GZY-M6617
GZY-S750
GZY-S750
GZY-LED PCB6020
GZY-LED PCB6020
GZY-S6025
GZY-S6025
GZY-A8654
GZY-A8654
GZY-Z3328
GZY-Z3328
GZY-Z1912
GZY-Z1912

GZY-Z3328
GZY-Z3328

GZY-Z5028
GZY-Z5028

GZY-Z7530
GZY-Z7530

GZY-Z6028
GZY-Z6028

GZY-Z8030
GZY-Z8030

GZY-C11045
GZY-C11045
Vehicle RFID self-adhesive label for 8-meter glass penetration, IP65 protection against extreme temperature changesProduct NumberGZY-D840
GZY-D840
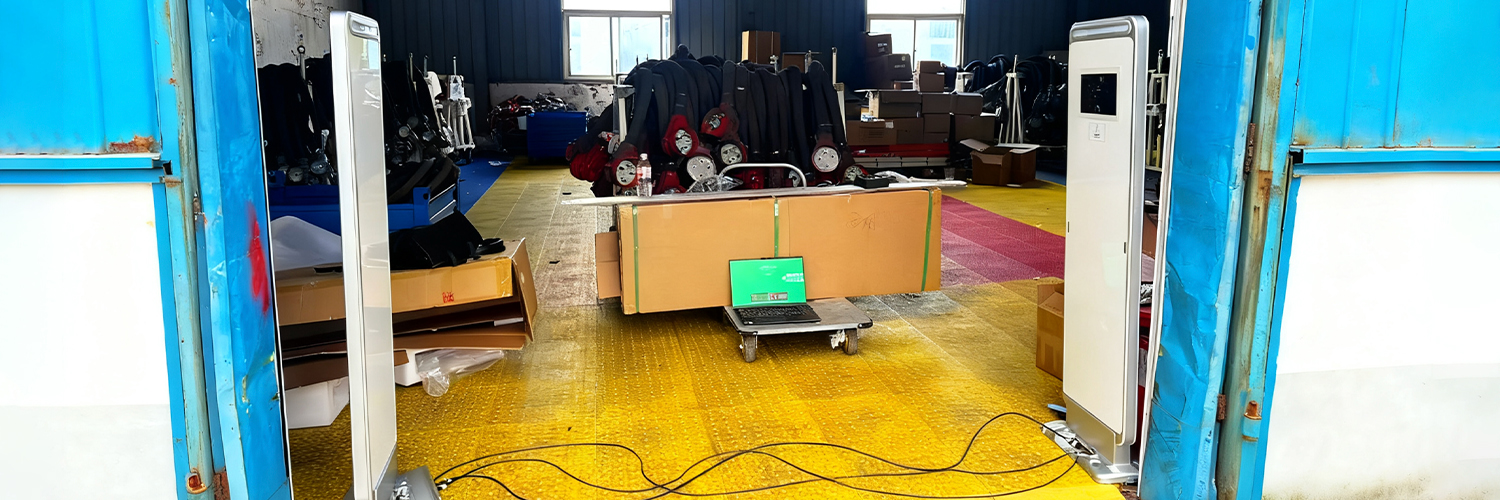
4-port RFID split-type reader 700 tags/second high-speed inventory Military-grade components ensure 365 days of non-stop operation
GZY-D880
GZY-D880
8-port RFID split-type reader 700 tags/second high-speed inventory Military-grade components ensure 365 days of non-stop operation
GZY-D816
GZY-D816
16-port RFID split-type reader 1000 tags/second high-speed inventory Military-grade components ensure 365 days of non-stop operation Product Number
Product NumberGZY-E609
GZY-E609
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, high-performance RFID integrated reader, all-weather operation, stable long-distance reading, applicable to access control, logistics and other applications.
GZY-605
GZY-605
The ultra-high frequency integrated reader series is a high-performance, all-weather industrial-grade fixed 5dBi reader.
GZY-E612
GZY-E612
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, high-performance RFID integrated reader, all-weather operation, stable long-distance reading, applicable to access control, logistics and other applications.
GZY-608
GZY-608
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, industrial RFID high-speed reader, IP65 protection with a 10-meter long-range, multi-mode intelligent control for vehicle logistics
GZY-612
GZY-612
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, RFID industrial-grade passive identification all-in-one machine, water-resistant and durable, with stable long-distance performance, supporting multiple protocols, suitable for access control, logistics and other scenarios
GZY-610
GZY-610
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, industrial-grade RFID integrated reader, rugged and durable, multi-mode support, suitable for intelligent warehousing and manufacturing.
GZY-E606
GZY-E606
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, industrial-grade RFID integrated reader, rugged and durable, multi-mode support, suitable for intelligent warehousing and manufacturing.
GZY-E607
GZY-E607
Ultra-high frequency integrated reader series, high-performance RFID integrated reader, all-weather operation, stable long-distance reading, applicable to access control, logistics and other applications. Product Number
Product NumberGZY-33
GZY-33
Specialized RFID reading and writing station for physical evidence, with a 400mm large surface and adjustable power of 33dBm.
GZY-77
GZY-77
RFID Desktop Reader-Writer Series RFID Card Issuance Device, Intelligent, Efficient, Flexible Communication
GZY-76
GZY-76
Desktop RFID card issuing machine, intelligent automatic label input, portable and efficient
GZY-31
GZY-31
RHID tag reader, compact 255mm body, 50 tags per second precise near-field inventory
GZY-32
GZY-32
Near-field RFID reader, 370mm high-efficiency group reading,one-click output on the simulated keyboard
GZY-36
GZY-36
An RFID checkout counter with a 600mm large-sized countertop, capable of batch binding 50 tags per second, has an IP54 protection rating and is suitable for general use in various scenarios.
GZY-D4L
GZY-D4L
An RFID checkout counter with a 600mm large-sized countertop, capable of batch binding 50 tags per second, has an IP54 protection rating and is suitable for general use in various scenarios.Product NumberGZY-202
GZY-202
RFID handheld terminal reader, with high processing performance, long tag reading distance and high group reading rate, is widely used in logistics, asset management and other scenarios.
GZY-122
GZY-122
RFID handheld terminal reader, with high processing performance, Multifunctional RFID warehouse inventory handheld device, integrating RFID and biometric identification,with excellent performance and stability.GZY-230
GZY-230

GZY-3100
GZY-3100

GZY-A6
GZY-A6
 Product Number
Product NumberGZY-T509
GZY-T509
RFID ultra-high frequency 9dBi antenna, with strong anti-aging and weather resistance, capable of stable operation in harsh environments.
GZY-T5050
GZY-T5050
GZY-T1010
GZY-T1010
GZY-T2020
GZY-T2020
GZY-T0505A
GZY-T0505A
GZY-T0303A
GZY-T0303A
GZY-T0808A
GZY-T0808A
GZY-T0909
GZY-T0909
GZY-T1111
GZY-T1111
GZY-T506
GZY-T506
GZY-T50
GZY-T50
GZY-T512
GZY-T512
RFID 12dBi identification antenna, made of aluminum-plastic composite material with anti-aging and weather-resistant properties, suitable for logistics/asset management and other scenarios. Product NumberProduct Number
Product NumberProduct NumberRFID Reader Modules
RFID Integrated devices
Product NumberProduct Number -
Application Solutions
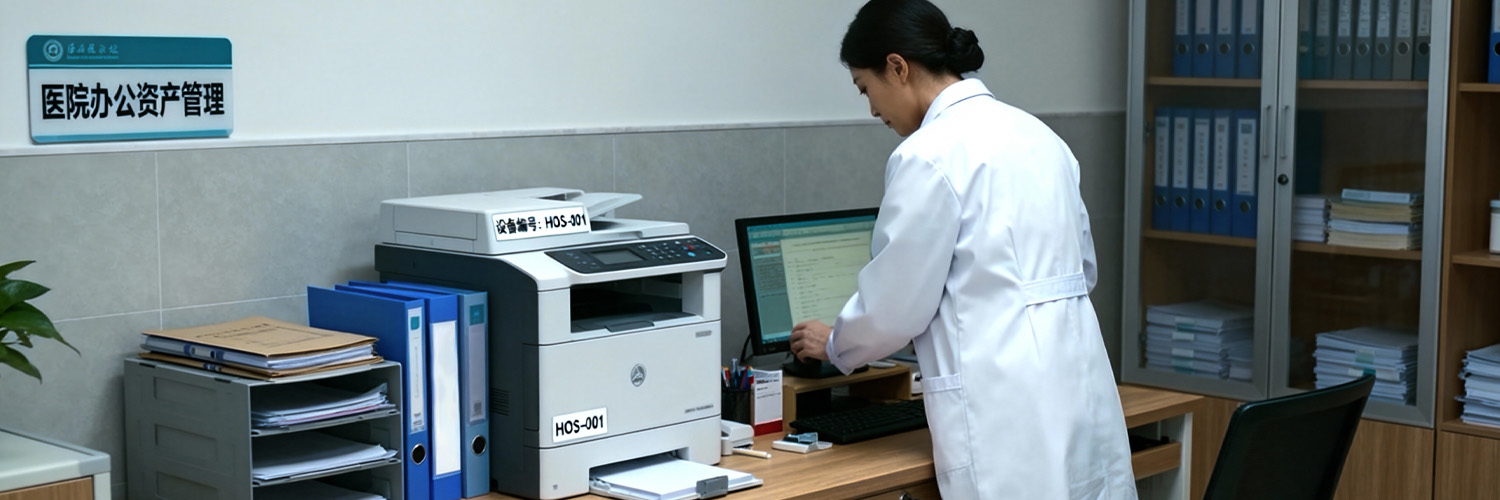
- Warehouse Asset Management
- Tool and Equipment Management
- Smart Port Terminal
- Personnel Location Management
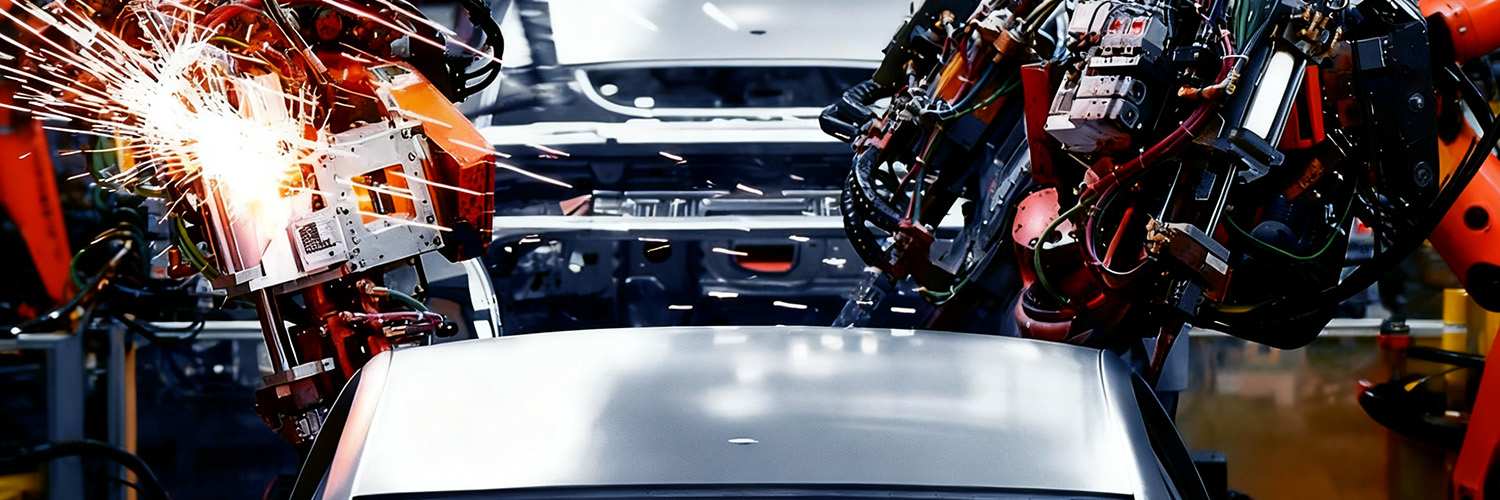
- Industry manufacture 4.0
- Smart Cleaning of Linens
- Clothing retail management
Tool and Equipment ManagementPersonnel Location ManagementIndustry manufacture 4.0Smart Cleaning of LinensClothing retail management -
Successful Cases
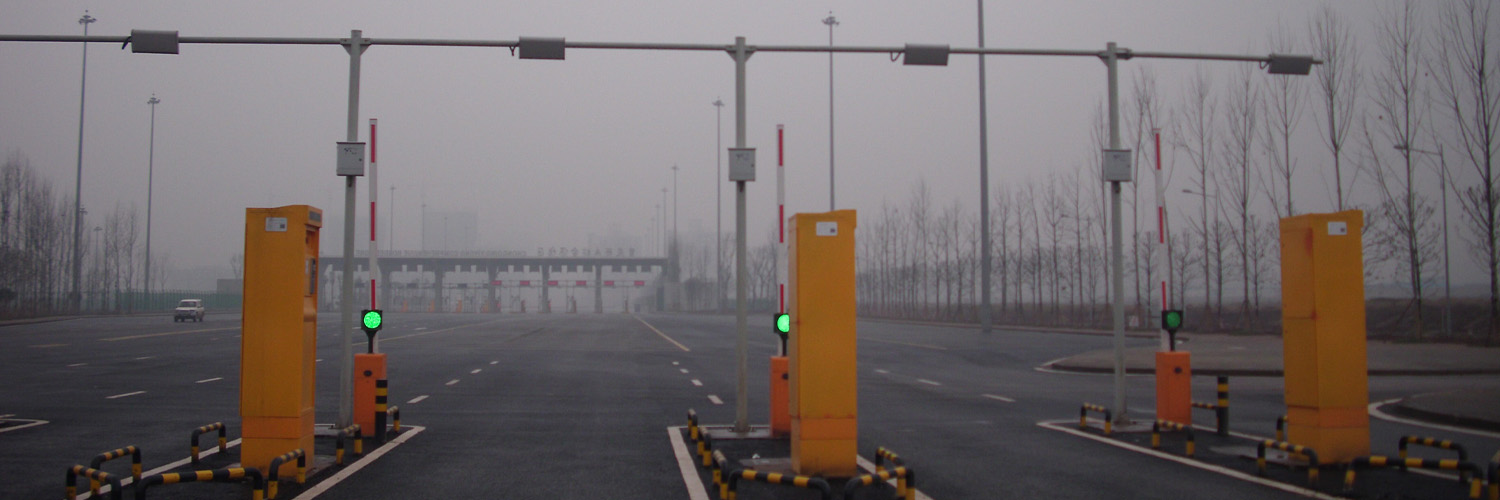
- Intelligence Port
- Warehouse Asset
- Production Line
- Smart garbage truck
- Tool Tracking
- Personnel management
Intelligence PortWarehouse AssetProduction LineSmart garbage truckTool TrackingPersonnel management - About Infowise
- Support
- Contact Us


































